蜉蝣系统发育-当前项目
This research aims to elucidate the phylogenetic relationships of the mayfly family Coloburiscidae (蜉蝣目)-有刺的有鳃的蜉蝣。 这个科由三个属组成: Murphyella Coloburiscoides, 和 Coloburiscus。 A unique characteristic of this family is that they demonstrate Gondwanan distribution being found in New Zeal和, Australia, Southern South America. In past studies, combined morphological 和 molecular data have questioned the family’s monophyly. The molecular data that has been used mostly comes from five “traditional” genes used in insect molecular phylogenetics. We compared our newly generated phylogenomic data to these traditional genes. We used targeted capture next generation sequencing to generate over 400 exons from the mayfly genome to create a large phylogenomic dataset. Bioinformatic software was used to align the data 和 carry out phylogenetic tree reconstruction using maximum likelihood, Bayesian, maximum parsimony analyses. The resulting trees support the monophyly of Coloburiscidae, confirming the hypothesis of this research.

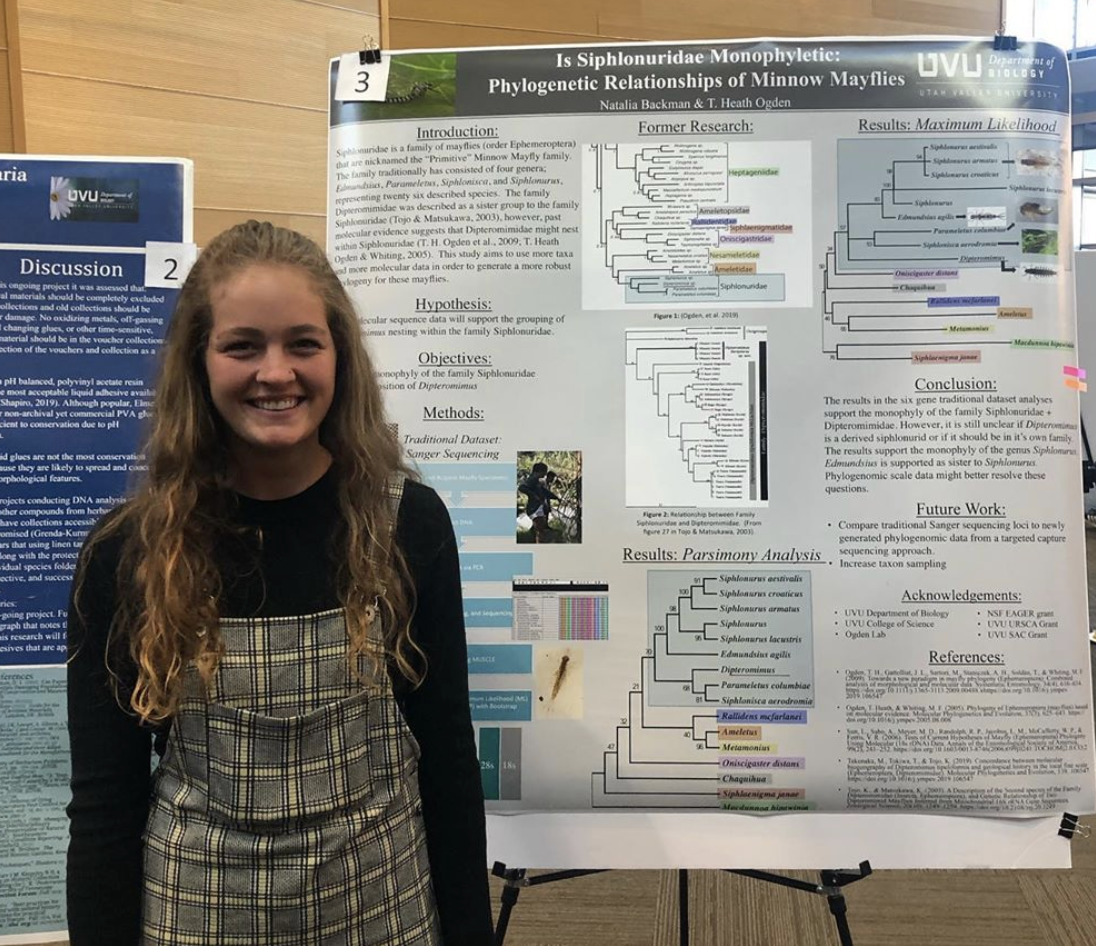
Siphlonuridae is a family of mayflies (order Ephemeroptera) that are nicknamed the “Primitive” Minnow Mayfly family. The family traditionally has consisted of four genera; Edmundsius, Parameletus, Siphlonisca, Siphlonurus,代表26个已被描述的物种。 The family Dipteromimidae was described as a sister group to the family Siphlonuridae (东城 & Matsukawa, 2003), however, past molecular evidence suggests that Dipteromimidae might nest within Siphlonuridae (t.h. Ogden et al., 2009; T. Heath Ogden & Whiting, 2005)。 This study aims to use more taxa 和 more molecular data in order to 生成更多 强健的系统发育 蜉蝣。
一般昆虫学
生物信息学
We are interested in using transcriptome data, generated with next generation sequencing technology, to investigate the evolutionary trends of specific genes 和 their associated expression in 蜉蝣。 我们为蜉蝣生成了一个额外的转录组。 RNA was extracted from a freshly frozen specimen preserved in RNA后来® (Ambion) using TRIzol® Reagent (Ambion) 和 cDNA libraries were prepared from mRNA. RNA-seq data was generated using a paired-end protocol (PE100) on Illumina HiSeq2000 with an expected 60 million reads. In order to effectively investigate the large amount of sequences, we created a bioinformatics workflow to analyze the newly generated transcriptome data along with previous data for 蜉蝣。 The workflow consists of these main steps: Trinity (Assembling the transcripts), Transdecoder (Identifying c和idate coding regions), HMMER (搜索ing biological sequence databases for homologous sequences). 我们测试了视蛋白基因的工作流程。

教学研究